Close search
 Published :
/
Published :
/ Posted by : Retech
Posted by : RetechDue to variations in natural climate conditions, geographical environments, and economic factors across different regions, broiler farming methods also differ significantly. The four most common broiler-raising methods are
Each method has its own advantages and disadvantages. Understanding these differences helps farmers make informed decisions and implement appropriate adjustments in their production systems.
Regardless of the breeding method used, careful management by the breeder is the most critical factor.
This breeding method requires less investment, is easy to operate, and is suitable for general farmers. It has low requirements for the height and width of the chicken house. However, proper selection and management of the litter is essential.

1.Ground preparation
(1) The ground must be solid, such as cement or red brick.
(2) The floor of the chicken house should be thoroughly cleaned and disinfected.
Chicken house disinfection steps
Checking the disinfection effect
(a) Expose the sterilized culture medium in the chicken house for 1 minute, then incubate at a constant temperature to determine the type and number of bacteria and evaluate the disinfection effect.
(b) Wipe the floor and walls with a sterilized warm cotton swab for 1-2 minutes, then soak it in 30 ml of saline for 5 minutes to test the total number of colonies, E. coli count, and Salmonella count.
2.Preparation of Litter
The litter should be of good quality, dry, soft, absorbent, clean, and free from dirt. It should not be moldy or deteriorated, and should be of appropriate length and thoroughly fumigated. One of the key measures for successful litter rearing is ensuring the quality of the litter. Commonly used ground litter includes rice husks, rice crumbs, husks, shredded wheat straw, broken corn cobs, leaves, dry weeds, and straw. In foreign countries, discarded tire particles or waste newspaper balls are also used as litter.
(1) Wood Chips: The first choice for litter. They should be soft and not moldy. If the source is inconvenient, they can only be used for brooding. The equipment should be well maintained when they are put out.
(2) Sawdust: Can be used as litter. Since newborn chicks are prone to accidentally eating sawdust, the box should be tightly sealed with padding paper.
(3) River Sand: Should be the same size and uniform. Dirt, stones, and other debris should be sieved out. To avoid contamination, it is best to sterilize it in the sun before use, but do not dry it too much to avoid dust.
(4) Sea Sand: Cleaner than river sand due to sun exposure and purification by seawater. It should be fully utilized if conditions permit.
(5) Peanut Shells, Bean Shells, Rice Husks: Should not be moldy. If the shells are too hard, they should be pressed before use.
(6) Wheat Straw, Rice Straw, Corn Straw: Should not be moldy and should be chopped into small pieces 3-6 cm long. Wheat straw should be chopped to remove the awns.
(7) Leaves: Such as poplar and peach leaves should not be moldy, and hard branches should be removed.
(8) Broken Corn Cobs: Can be used as litter.
(9) Alternative Materials: Some people use discarded tire particles or waste newspaper balls as padding. The above materials can also be used in combination.
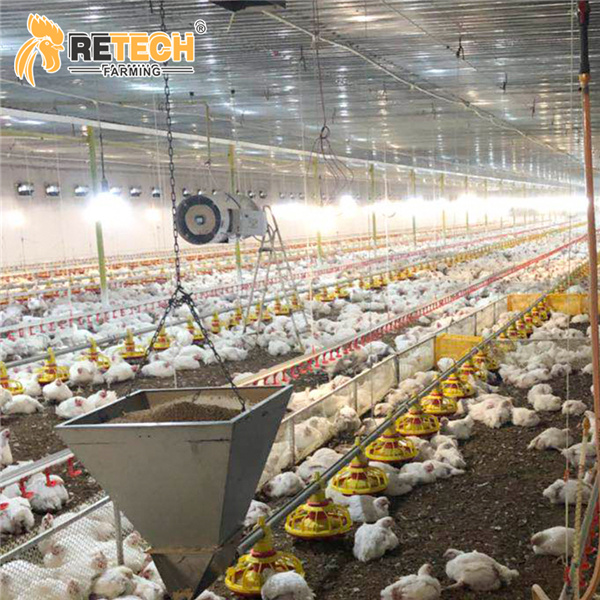

3.Use of Litter
Clean the floor of the chicken house and disinfect it thoroughly, then lay a layer of litter about 10 cm thick on the floor. The chickens will live on the litter from the time they enter the house until they are sold. Be careful not to make the litter too thick, as it could hinder the chickens' activities or even cause accidents if the chicks get covered by the litter. As the chickens grow older, the litter gets trampled, its thickness decreases, and the amount of feces increases. New litter should be added regularly. Generally, after the chicks are 2 to 3 weeks old, add new litter every 3 to 5 days to maintain a thickness of 15 to 20 cm. Once the broilers are grown and ready to be released, remove the feces and litter all at once, and do not replace them in the middle.
4.Management of Litter
During daily management, the litter should be turned over frequently. Wet litter near the water source should be regularly replaced with drier litter to prevent it from becoming too wet and clumped together. Also, ensure that fire precautions are taken during heating and fumigation to avoid burning the litter. The litter should be kept dry, soft, flat, and not hardened or exposed to the ground. Replace wet litter with fresh litter promptly. If the litter becomes too thin, the chicken farming environment will suffer. With less litter and more feces, the chicken house will become damp, and ammonia concentration may exceed safe levels, negatively impacting the growth and development of broiler chickens. This can lead to disease outbreaks and even large-scale deaths. Additionally, damp and thin litter can cause breast cysts in broiler chickens. Special care should be taken to prevent the litter from getting wet. Ensure there is a waterproof layer in the ground structure, and manage the waterers strictly to control any water leakage and prevent the litter from becoming wet when the chickens drink water.
5.Advantages of Ground Bedding
(1) Broilers grow quickly, are docile, and are not very active, making ground breeding particularly suitable for them.
(2) Ground bedding promotes the development of broiler legs; the fermentation of bedding and feces generates heat, helping to increase room temperature.
(3) The activity of microorganisms in the bedding produces vitamin B, which can be ingested by broilers as they turn over the bedding.
(4) The system is simple, labor-saving, easy to operate, and requires low investment. It is easy to manage, puts little stress on the chickens, helps them gain weight quickly, and leads to a high survival rate.
(5) Bedding materials are widely available. Farmers can use agricultural by-products such as rice straw and wheat straw, which not only reduces air pollution from burning these materials but also saves costs.
(6) The incidence of breast cysts, keel bending, and leg diseases is reduced, and fewer defective broilers are produced.
6.Disadvantages of Ground Bedding
(1) It takes up a lot of space, consumes significant energy, and is difficult to source and process.
(2) Broilers are in direct contact with feces, making it challenging to control coccidiosis, and the cost of medication and bedding can be high.
(3) Vaccination is time-consuming and labor-intensive.
Plastic net floor farming involves raising broilers on a flat net at a certain height from the ground. While the incidence of leg diseases and chest swelling in plastic net floor farming is higher than in ground flat farming, a comprehensive comparison shows that plastic net floor farming still offers more advantages than disadvantages when compared to both ground flat farming and cage farming.
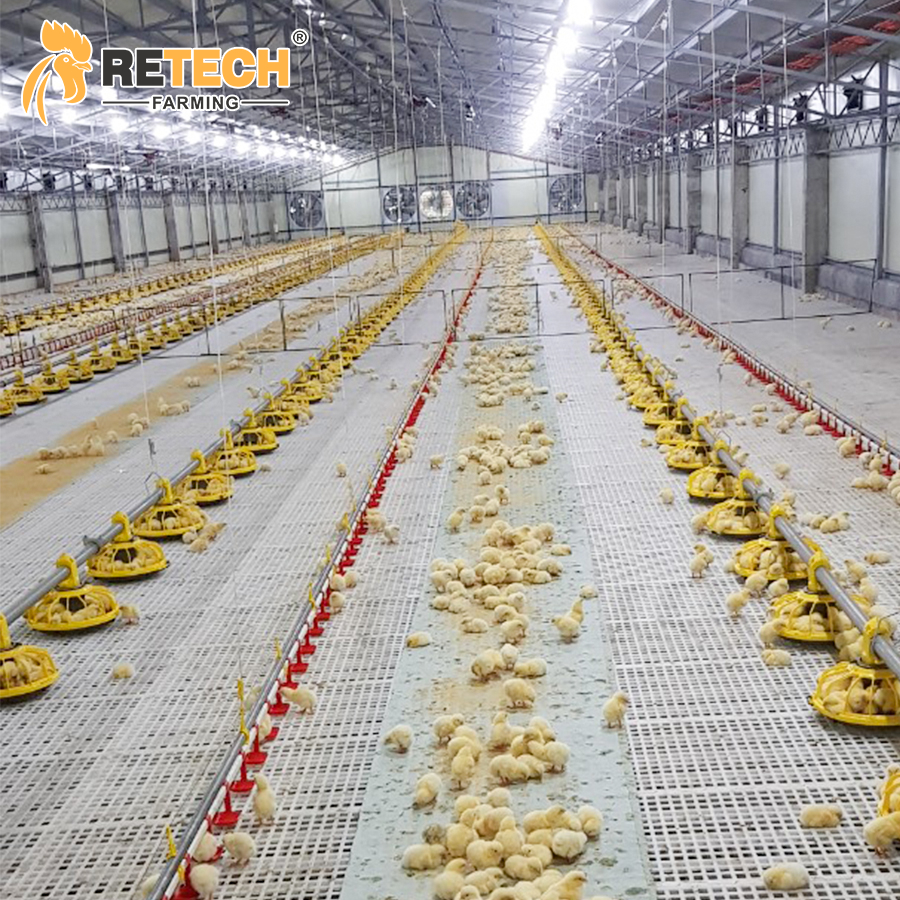

1.Setting up the plastic net
2.Advantages of flat farming on the net:
3.Disadvantages of flat farming on the net:
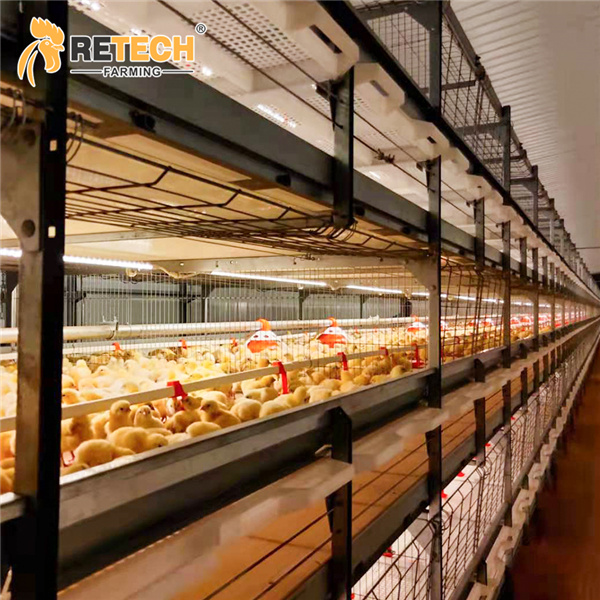
Cage farming is a method of raising broilers in cages, where chickens are housed in cages from hatching until they are sold. As they grow older and heavier, they are typically raised using rotating layers or cages. This is a relatively advanced breeding method that makes efficient use of the space in the chicken house. Although the stocking density is higher than in ground-based or net-based farming, the equipment investment is relatively large.
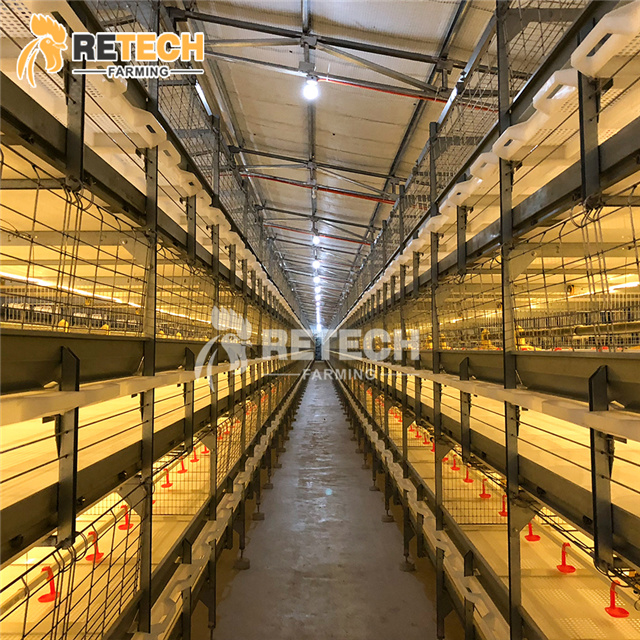

1.Types of cages
2.Advantages of cage breeding
(1) The stocking density is nearly 1.5 times higher than that of flat-raising. The feeding volume per unit area can be increased by about 1.5 times, which effectively improves the utilization rate of the chicken house.
(2) Since chickens are confined to a cage, they have limited space for movement, consume less energy, and reduce competition for food. This results in better growth, easier fattening, and higher weight gain, which can improve feeding efficiency by 5%–10% and reduce total costs by 3%–7%.


So if you are looking for poultry chicken business opportunity, and if you want to start your own poultry chicken business, pls feel free to give us a call, below is our contact information:
Website: www.retechfarming.com
Facebook: @retechfarmingchickencage 100k Followers